Redshift
In order to have set up a Redshift connection, you need to add a configuration item to connections in the .bruin.yml file complying with the following schema Mind that, despite the connection being at all effects a Postgres connection, the default port field of Amazon Redshift is 5439.
connections:
redshift:
- name: "connection_name"
username: "awsuser"
password: "XXXXXXXXXX"
host: "redshift-cluster-1.xxxxxxxxx.eu-north-1.redshift.amazonaws.com"
port: 5439
database: "dev"
ssl_mode: "allow"ssl_mode should be one of the modes describe in the postgres documentation.
Making Redshift publicly accessible
Before the connection works properly, you need to ensure that the Redshift cluster can be access from the outside. In order to do that you must mark the configuration option in your redshift cluster
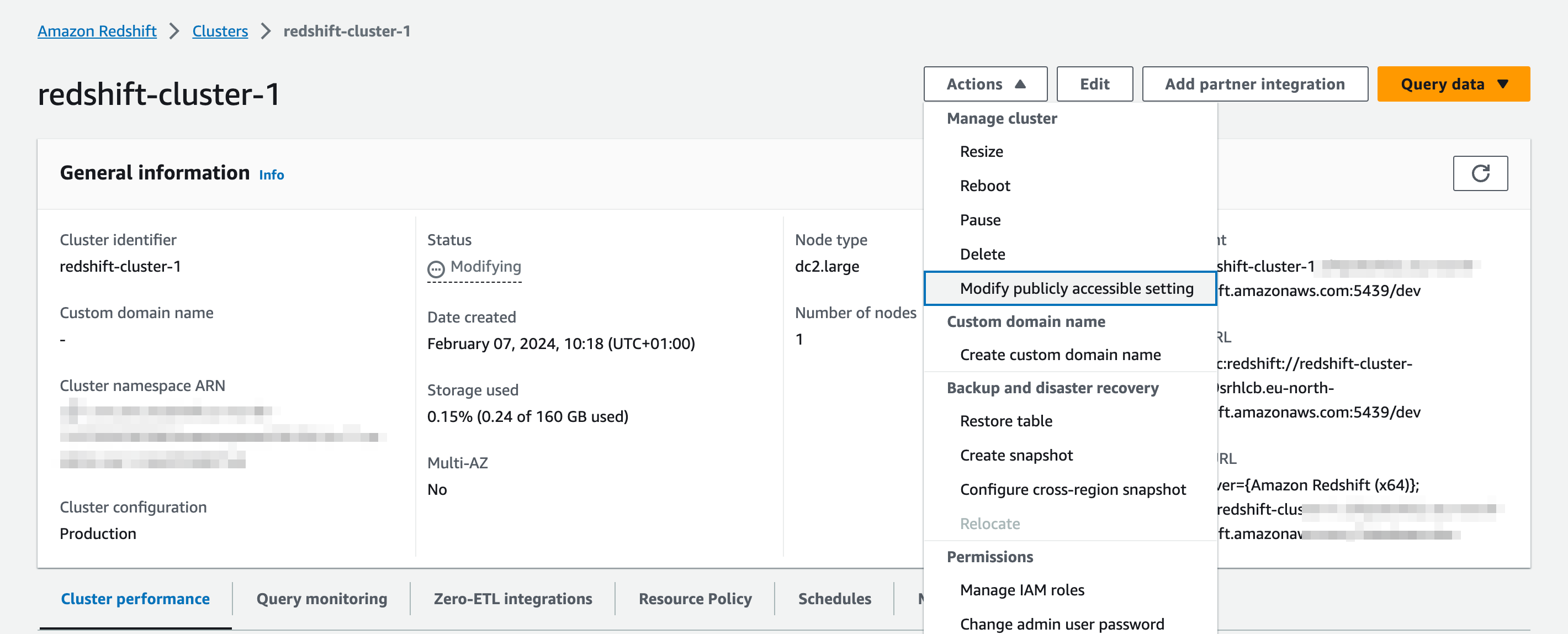
In addition to this, you must configure the inbound rules of the security group your redshift cluster belongs to, to accept inbound connections. In the example below we enabled access for all origins but you can set more restrictive rules for this.
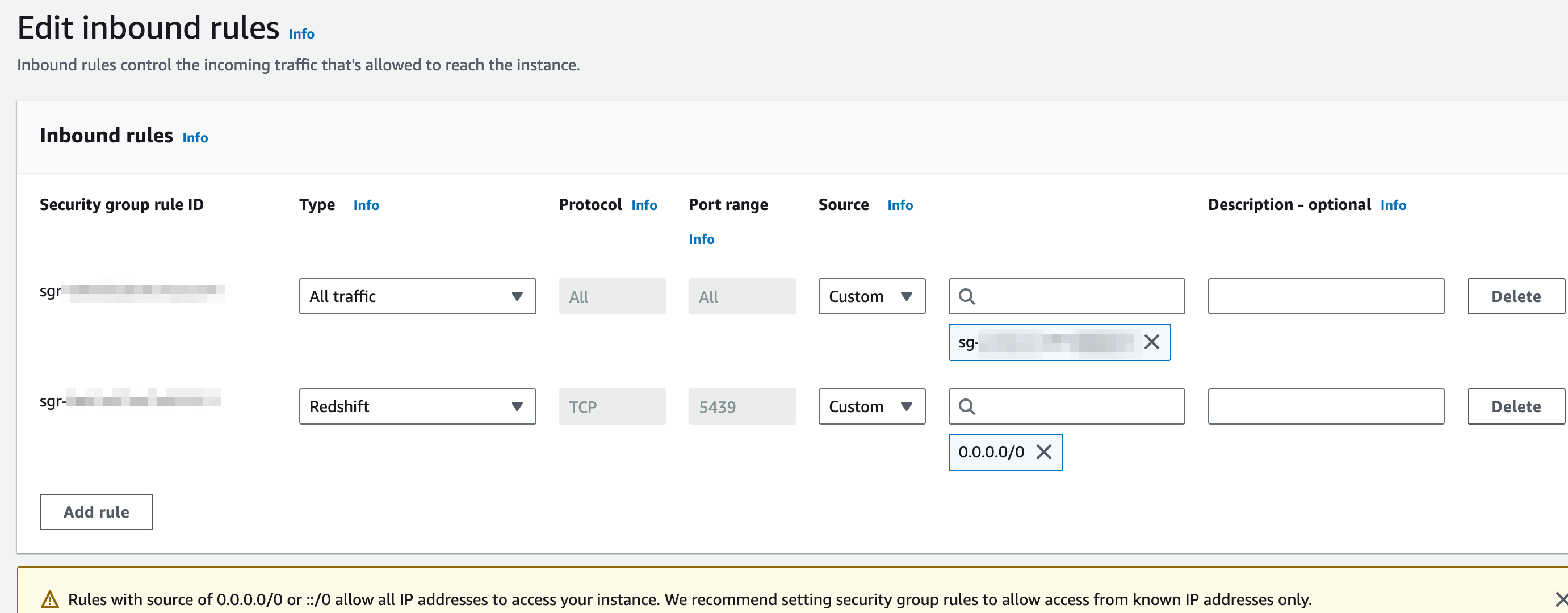
If you have trouble setting this up you can check Aws documentation on the topic